1. Soviet deportations from Lithuania 1941 and 1944-1953
2. Beginning This string of tragedies began in August 1939,when Hitler and Stalin concluded a cynicalagreement that divided up Central Europe betweenthe two totalitarian countries. According to theMolotov-Ribbentrop pact, Lithuania was to fall intothe Soviet zone of influence.
3. The total number of persons registered as “anti-Soviet elements” reached 320,000 entries. Therewere teachers and professors, school and collegestudents, farmers, industry workers and craftsmenamong them.
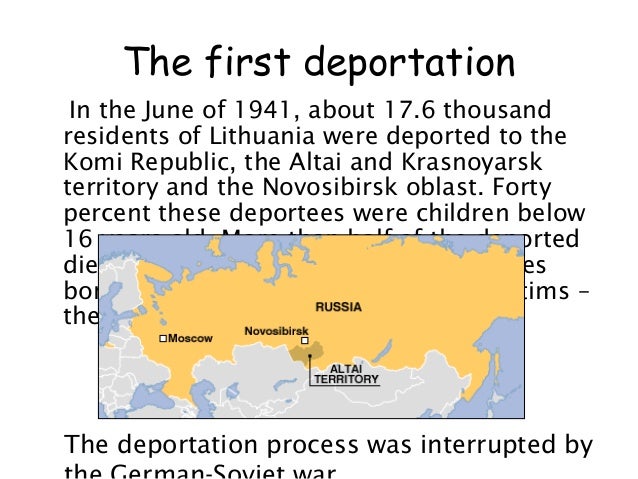
4. The first deportation In the June of 1941, about 17.6 thousandresidents of Lithuania were deported to theKomi Republic, the Altai and Krasnoyarskterritory and the Novosibirsk oblast. Fortypercent these deportees were children below16 years old. More than half of the deporteddied quickly. Pregnant women and babiesborn in the cattle cars were the first victims –they died in the trains.The deportation process was interrupted by
5. The largest deportations from Lithuania• “Spring” (“Vesna”) – May 22-23rd, 1948• “Surf” (“Priboj”) - March-April, 1949• “Autumn” (“Osen”) - October 2-3, 1951
6. “Spring” In 1948, May 22-23rd, adeportationsoperation called"Vesna" (“Spring”)took place. It wasplanned to deport12 134 families(48 thousandpeople) to Yakutia(later changedinto Buryat-Mongolia
7. “Surf” During the1949 March-Aprildeportations(operation"Priboj"), around32 thousandpeople (10thousandfamilies) weredeported fromLithuania. Itsaim was tosuppress thewealthy
8. 1951 winterKrasnoyarsk territory, Kamenka village
9. This is a living place of deportees in a forestry in Taiga.
10. A funeral ceremony Ready for school
11. Last days in Siberia
12. “Autumn” While carryingout thedeportationoperation called"Osen"(“Autumn”), onOctober 2-3,1951, more than16 thousandpeople (about5.3 thousandchildren amongthem) were
13. How did the typical deportation look? The NKVD broke intoan apartment orhouse and arrestedall the familymembers. In the railway stationas far as the eyecould see there weremen and women, theelderly and thedisabled searching
14. What did the deportees do? Worked in salt and coal mines, collective farms, woods. Cut wood and sailed rafts. Built roads and railways in Taiga. Worked in Fishing farms.
15. Consequences of the deportations Total 132,000 Lithuanians were deported to remote areas of the USSR: Siberia, the Arctic Circle zone and Central Asia. More than 70 percent of the deportees were women and children. Around 50,000 of the deportees were not able to return to Lithuania ever again. Every third Lithuanian became a victim of Soviet terror. The lithuanians feel the moral harm of these tragic events till nowadays.





slideshare
vilnews
2. Beginning This string of tragedies began in August 1939,when Hitler and Stalin concluded a cynicalagreement that divided up Central Europe betweenthe two totalitarian countries. According to theMolotov-Ribbentrop pact, Lithuania was to fall intothe Soviet zone of influence.
3. The total number of persons registered as “anti-Soviet elements” reached 320,000 entries. Therewere teachers and professors, school and collegestudents, farmers, industry workers and craftsmenamong them.
4. The first deportation In the June of 1941, about 17.6 thousandresidents of Lithuania were deported to theKomi Republic, the Altai and Krasnoyarskterritory and the Novosibirsk oblast. Fortypercent these deportees were children below16 years old. More than half of the deporteddied quickly. Pregnant women and babiesborn in the cattle cars were the first victims –they died in the trains.The deportation process was interrupted by
5. The largest deportations from Lithuania• “Spring” (“Vesna”) – May 22-23rd, 1948• “Surf” (“Priboj”) - March-April, 1949• “Autumn” (“Osen”) - October 2-3, 1951
6. “Spring” In 1948, May 22-23rd, adeportationsoperation called"Vesna" (“Spring”)took place. It wasplanned to deport12 134 families(48 thousandpeople) to Yakutia(later changedinto Buryat-Mongolia
7. “Surf” During the1949 March-Aprildeportations(operation"Priboj"), around32 thousandpeople (10thousandfamilies) weredeported fromLithuania. Itsaim was tosuppress thewealthy
8. 1951 winterKrasnoyarsk territory, Kamenka village
9. This is a living place of deportees in a forestry in Taiga.
10. A funeral ceremony Ready for school
11. Last days in Siberia
12. “Autumn” While carryingout thedeportationoperation called"Osen"(“Autumn”), onOctober 2-3,1951, more than16 thousandpeople (about5.3 thousandchildren amongthem) were
13. How did the typical deportation look? The NKVD broke intoan apartment orhouse and arrestedall the familymembers. In the railway stationas far as the eyecould see there weremen and women, theelderly and thedisabled searching
14. What did the deportees do? Worked in salt and coal mines, collective farms, woods. Cut wood and sailed rafts. Built roads and railways in Taiga. Worked in Fishing farms.
15. Consequences of the deportations Total 132,000 Lithuanians were deported to remote areas of the USSR: Siberia, the Arctic Circle zone and Central Asia. More than 70 percent of the deportees were women and children. Around 50,000 of the deportees were not able to return to Lithuania ever again. Every third Lithuanian became a victim of Soviet terror. The lithuanians feel the moral harm of these tragic events till nowadays.







slideshare
vilnews
Komentarų nėra:
Rašyti komentarą